A Dna Origami Plasmonic Sensor With Environment-independent Read-ou
Abstract
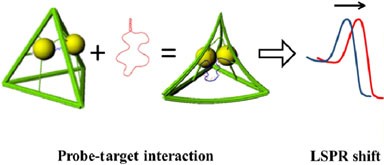
DNA origami is a promising technology for its reproducibility, flexibility, scalability and biocompatibility. Among the several potential applications, DNA origami has been proposed as a tool for drug delivery and as a contrast agent, since a conformational change upon specific target interaction may be used to release a drug or produce a physical signal, respectively. However, its conformation should be robust with respect to the properties of the medium in which either the recognition or the read-out take place, such as pressure, viscosity and any other unspecific interaction other than the desired target recognition. Here we report on the read-out robustness of a tetragonal DNA-origami/gold-nanoparticle hybrid structure able to change its configuration, which is transduced in a change of its plasmonic properties, upon interaction with a specific DNA target. We investigated its response when analyzed in three different media: aqueous solution, solid support and viscous gel. We show that, once a conformational variation is produced, it remains unaffected by the subsequent physical interactions with the environment.
References
- [1]
Ghosh, S. K.; Pal, T. Interparticle coupling effect on the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles: From theory to applications. Chem Rev. 2007, 107, 4797–4862.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [2]
Reinhard, B. M.; Siu, M.; Agarwal, H.; Alivisatos, A. P.; Liphardt, J. Calibration of dynamic molecular rulers based on plasmon coupling between gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2246–2252.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [3]
Prodan, E.; Radloff, C.; Halas, N. J.; Nordlander, P. A hybridization model for the plasmon response of complex nanostructures. Science 2003, 302, 419–422.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [4]
Hill, R. T.; Mock, J. J.; Hucknall, A.; Wolter, S. D.; Jokerst, N. M.; Smith, D. R.; Chilkoti, A. Plasmon ruler with angstrom length resolution. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9237–9246.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [5]
Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Chowdhury, M. H.; Lakowicz, J. R. Metal-enhanced single-molecule fluorescence on silver particle monomer and dimer: Coupling effect between metal particles. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2101–2107.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [6]
Lim, D. K.; Jeon, K. S.; Kim, H. M.; Nam, J. M.; Suh, Y. D. Nanogap-engineerable Raman-active nanodumbbells for single-molecule detection. Nat Mater. 2010, 9, 60–67.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [7]
Taminiau, T. H.; Stefani, F. D.; Segerink, F. B.; Van Hulst, N. F. Optical antennas direct single-molecule emission. Nat Photonics 2008, 2, 234- 237.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [8]
Bek, A.; Jansen, R.; Ringler, M.; Mayilo, S.; Klar, T. A.; Feldmann, J. Fluorescence enhancement in hot spots of AFM-designed gold nanoparticle sandwiches. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 485–490.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [9]
Ding, B. Q.; Deng, Z. T.; Yan, H.; Cabrini, S.; Zuckermann, R. N.; Bokor, J. Gold nanoparticle self-similar chain structure organized by DNA origami. J Am Chem Soc. 2010, 132, 3248–3249.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [10]
Zhou, C.; Duan, X. Y.; Liu, N. A plasmonic nanorod that walks on DNA origami. Nat Commun. 2015, 6, 8102.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [11]
Kuzyk, A.; Schreiber, R.; Fan, Z. Y.; Pardatscher, G.; Roller, E. M.; Högele, A.; Simmel, F. C.; Govorov, A. O.; Liedl, T. DNA-based self-assembly of chiral plasmonic nanostructures with tailored optical response. Nature 2012, 483, 311–314.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [12]
Rothemund, P. W. K. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 2006, 440, 297–302.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [13]
Zanacchi, F. C.; Manzo, C.; Alvarez, A. S.; Derr, N. D.; Garcia-Parajo, M. F.; Lakadamyali, M. A DNA origami platform for quantifying protein copy number in super-resolution. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 789–792.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [14]
Hudoba, M. W.; Luo, Y.; Zacharias, A.; Poirier, M. G.; Castro, C. E. Dynamic DNA origami device for measuring compressive depletion forces. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 6566–6573.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [15]
Hong, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. DNA origami: Scaffolds for creating higher order structures. Chem Rev. 2017, 11 7, 12584–12640.
Google Scholar
- [16]
Jiang, Q.; Song, C.; Nangreave, J.; Liu, X. W.; Lin, L.; Qiu, D. L.; Wang, Z. G.; Zou, G. Z.; Liang, X. J.; Yan, H. et al. DNA origami as a carrier for circumvention of drug resistance. J Am Chem Soc. 2012, 134, 13396- 13403.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [17]
Hemmig, E. A.; Fitzgerald, C.; Maffeo, C.; Hecker, L.; Ochmann, S. E.; Aksimentiev, A.; Tinnefeld, P.; Keyser, U. F. Optical voltage sensing using DNA origami. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 1962–1971.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [18]
Marini, M.; Piantanida, L.; Musetti, R.; Bek, A.; Dong, M. D.; Besenbacher, F.; Lazzarino, M.; Firrao, G. A revertible, autonomous, self-assembled DNA-origami nanoactuator. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 5449- 5454.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [19]
Torelli, E.; Marini, M.; Palmano, S.; Piantanida, L.; Polano, C.; Scarpellini, A.; Lazzarino, M.; Firrao, G. A DNA origami nanorobot controlled by nucleic acid hybridization. Small 2014, 10, 2918–2926.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [20]
Prinz, J.; Schreiber, B.; Olejko, L.; Oertel, J.; Rackwitz, J.; Keller, A.; Bald, I. DNA origami substrates for highly sensitive surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Phys Chem Lett. 2013, 4, 4140–4145.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [21]
Acuna, G. P.; Möller, F. M.; Holzmeister, P.; Beater, S.; Lalkens, B.; Tinnefeld, P. Fluorescence enhancement at docking sites of DNA-directed self-assembled nanoantennas. Science 2012, 338, 506–510.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [22]
Piantanida, L.; Naumenko, D.; Lazzarino, M. Highly efficient gold nanoparticle dimer formation via DNA hybridization. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 15281–15287.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [23]
Sönnichsen, C.; Reinhard, B. M.; Liphardt, J.; Alivisatos, A. P. A molecular ruler based on plasmon coupling of single gold and silver nanoparticles. Nat Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 741–745.
Article Google Scholar
- [24]
Kuzyk, A.; Urban, M. J.; Idili, A.; Ricci, F.; Liu, N. Selective control of reconfigurable chiral plasmonic metamolecules. Sci Adv. 2017, 3, e1602803.
Article Google Scholar
- [25]
Zhou, C.; Xin, L.; Duan, X. Y.; Urban, M. J.; Liu, N. Dynamic plasmonic system that responds to thermal and aptamer-target regulations. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7395–7399.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [26]
Schreiber, R.; Luong, N.; Fan, Z. Y.; Kuzyk, A.; Nickels, P. C.; Zhang, T.; Smith, D. M.; Yurke, B.; Kuang, W.; Govorov, A. O. et al. Chiral plasmonic DNA nanostructures with switchable circular dichroism. Nat Commun. 2013, 4, 2948.
- [27]
Piantanida, L.; Naumenko, D.; Torelli, E.; Marini, M.; Bauer, D. M.; Fruk, L.; Firrao, G.; Lazzarino, M. Plasmon resonance tuning using DNA origami actuation. Chem Commun. 2015, 51, 4789–4792.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [28]
Kim, D. N.; Kilchherr, F.; Dietz, H.; Bathe, M. Quantitative prediction of 3D solution shape and flexibility of nucleic acid nanostructures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 2862–2868.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [29]
Castro, C. E.; Kilchherr, F.; Kim, D. N.; Shiao, E. L.; Wauer, T.; Wortmann, P.; Bathe, M.; Dietz, H. A primer to scaffolded DNA origami. Nat Methods 2011, 8, 221–229.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [30]
Masciotti, V.; Naumenko, D.; Lazzarino, M.; Piantanida, L. Tuning gold nanoparticles plasmonic properties by DNA nanotechnology. In DNA Nanotechnology: Methods and Protocols. Zuccheri, G., Ed.; Springer: New York, N Y, 2018; pp 279–297.
Chapter Google Scholar
- [31]
Dubochet, J.; Adrian, M.; Chang, J. J.; Homo, J. C.; Lepault, J.; McDowall, A. W.; Schultz, P. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens. Quart Rev Biophys. 1988, 21, 129–228.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [32]
Glaeser, R. M. Retrospective: Radiation damage and its associated "information limitations". J Struct Biol. 2008, 163, 271–276.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [33]
Lei, D. S.; Marras, A. E.; Liu, J. F.; Huang, C. M.; Zhou, L. F.; Castro, C. E.; Su, H. J.; Ren, G. Three-dimensional structural dynamics of DNA origami Bennett linkages using individual-particle electron tomography. Nat Commun. 2018, 9, 592.
- [34]
Zhang, L.; Lei, D. S.; Smith, J. M.; Zhang, M.; Tong, H. M.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Z. Y.; Liu, J. K.; Alivisatos, A. P.; Ren, G. Three-dimensional structural dynamics and fluctuations of DNA-nanogold conjugates by individual-particle electron tomography. Nat Commun. 2016, 7, 11083.
- [35]
Amenitsch, H.; Rappolt, M.; Kriechbaum, M.; Mio, H.; Laggner, P.; Bernstorff, S. First performance assessment of the small-angle X-ray scattering beamline at ELETTRA. J Synchrotron Radiat. 1998, 5, 506- 508.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [36]
Bernstorff, S.; Amenitsch, H.; Laggner, P. High-throughput asymmetric double-crystal monochromator of the SAXS beamline at ELETTRA. J Synchrotron Radiat. 1998, 5, 1215–1221.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [37]
Forget, A.; Pique, R. A.; Ahmadi, V.; Lüdeke, S.; Shastri, V. P. Mechanically tailored agarose hydrogels through molecular alloying with β-sheet polysaccharides. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 196–203.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [38]
Rüther, A.; Forget, A.; Roy, A.; Carballo, C.; Mießmer, F.; Dukor, R. K.; Nafie, L. A.; Johannessen, C.; Shastri, V. P.; Lüdeke, S. Unravelling a direct role for polysaccharide β-strands in the higher order structure of physical hydrogels. Angew Chem., Int Ed. 2017, 56, 4603–4607.
Article Google Scholar
- [39]
Mie, G. Beiträge zur Optik trüber Medien, speziell kolloidaler Metallösungen. Ann Phys. 1908, 330, 377–445.
Article Google Scholar
- [40]
García De Abajo, F. J. Multiple scattering of radiation in clusters of dielectrics. Phys Rev B 1999, 60, 6086–6102.
Article Google Scholar
- [41]
Myroshnychenko, V.; Rodríguez-Fernández, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Funston, A. M.; Novo, C.; Mulvaney, P.; Liz-Marzán, L. M.; García De Abajo, F. J. Modelling the optical response of gold nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev. 2008, 37, 1792–1805.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [42]
Walsh, A. S.; Yin, H. F.; Erben, C. M.; Wood, M. J. A.; Turberfield, A. J. DNA cage delivery to mammalian cells. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5427–5432.
CAS Article Google Scholar
- [43]
Lee, H.; Lytton-Jean, A. K. R.; Chen, Y.; Love, K. T.; Park, A. I.; Karagiannis, E. D.; Sehgal, A.; Querbes, W.; Zurenko, C. S.; Jayaraman, M. et al. Molecularly self-assembled nucleic acid nanoparticles for targeted in vivo siRNA delivery. Nat Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 389–393.
CAS Article Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
V. M. acknowledges financial support from MIUR (MIUR Giovani-Ambito "Salute dell'uomo"). Work at the Molecular Foundry, under the research project No. 3376, was supported by the Office of Science, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, of the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract No. DE-AC02-05CH11231. We acknowledge the Facility of Nanofabrication (FNF) of IOM for the support in sample preparation, Simone Dal Zilio and Silvio Greco for help in data analysis and stimulating discussions. We acknowledge Prof. Giuseppe Firrao for valuable comments and inspiring ideas, the NanoInnovation laboratory (Elettra Sincrotrone) for suggestion provided for AFM analysis and the BioLab (Elettra Sincrotrone) for the use of lab and instrumentation.
Electronic Supplementary Material
About this article
Cite this article
Masciotti, V., Piantanida, L., Naumenko, D. et al. A DNA origami plasmonic sensor with environment-independent read-out. Nano Res. 12, 2900–2907 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2535-0
Download citation
-
Received:
-
Revised:
-
Accepted:
-
Published:
-
Issue Date:
-
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-019-2535-0
Keywords
- DNA origami
- plasmonic sensor
- molecular detection
- gold nanoparticle
A Dna Origami Plasmonic Sensor With Environment-independent Read-ou
Source: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12274-019-2535-0
Belum ada Komentar untuk "A Dna Origami Plasmonic Sensor With Environment-independent Read-ou"
Posting Komentar